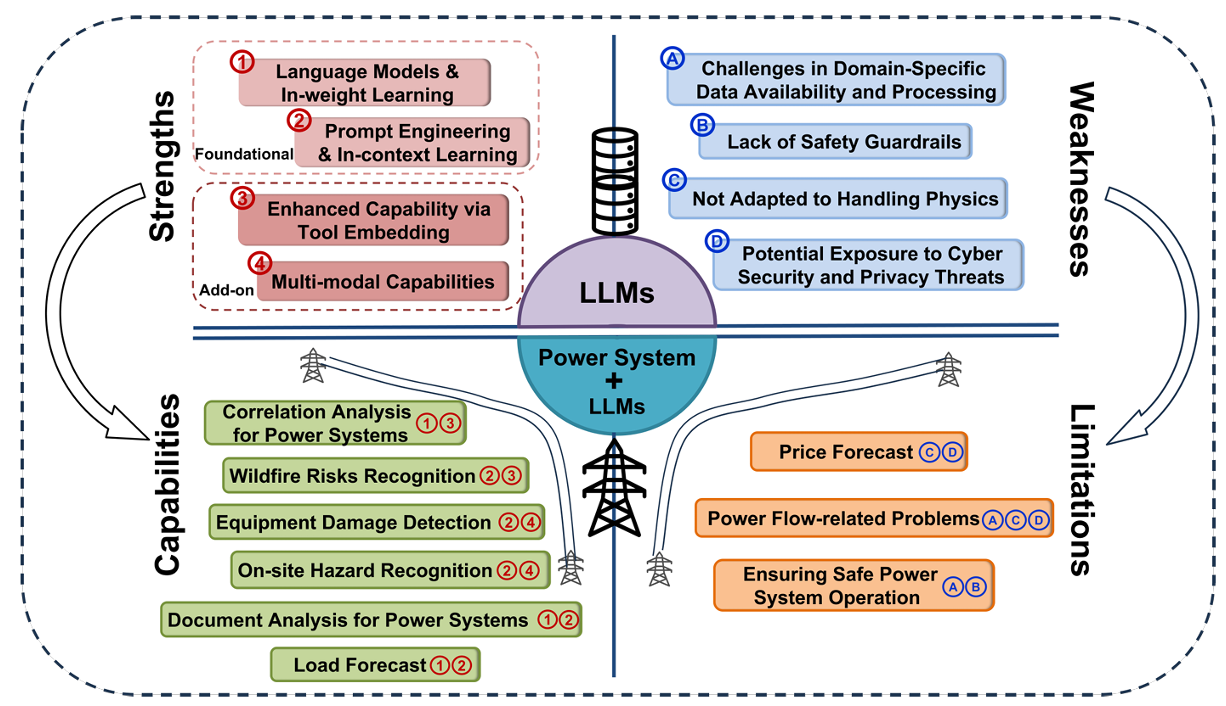
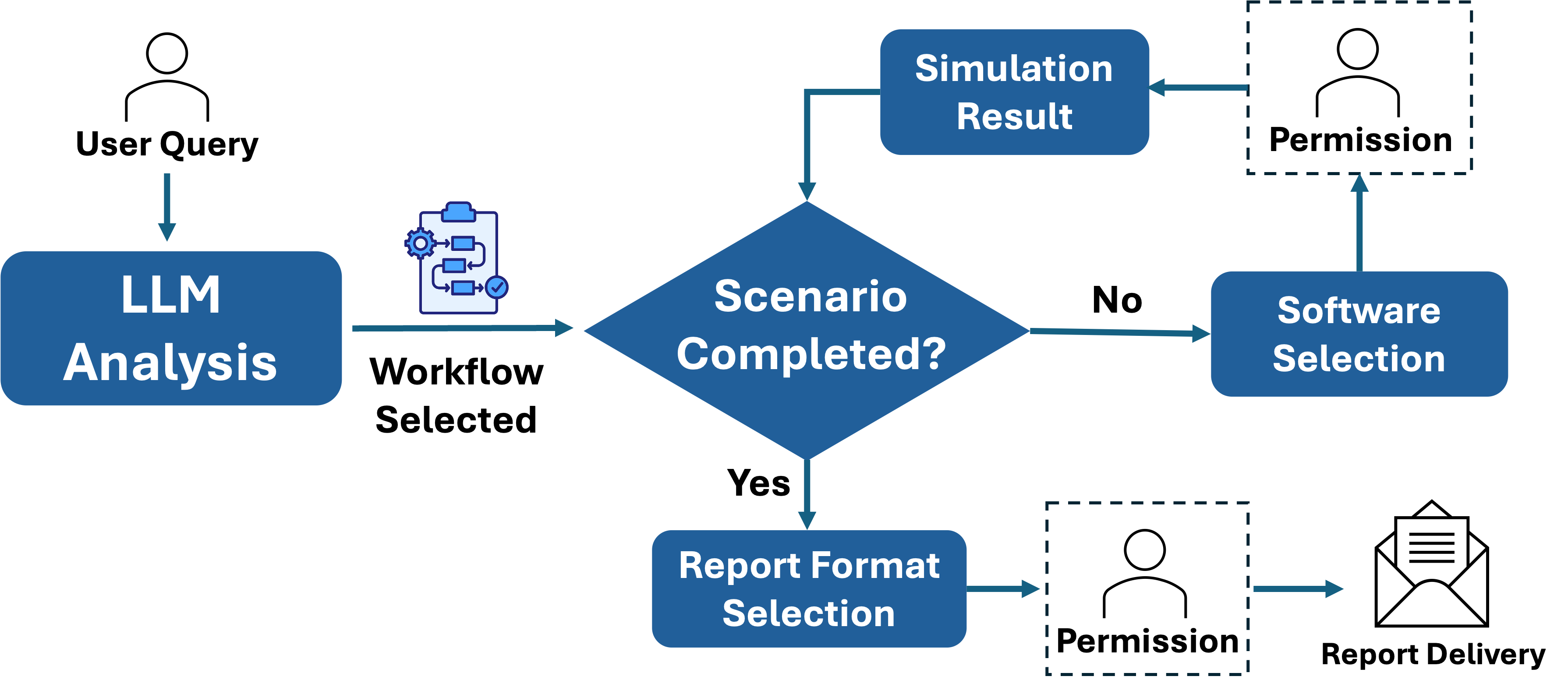
PowerAgent is an open-source community dedicated to accelerating the development of LLM-powered Tools and Agentic AI in the power systems domain. We aim to bridge the gap between cutting-edge AI and the real-world needs of system operators, electric utilities, and researchers, by creating a shared ecosystem of protocols, models, and workflows tailored for power applications.We believe the future of agentic AI in power domain will be driven by the combined development and coordination of three key components — Foundation Models (FM), Model Context Protocol (MCP), and Workflows (WF).
[1] Qian
Zhang and Le Xie. "PowerAgent: A Road Map Toward Agentic Intelligence in Power Systems: Foundation
Model, Model Context Protocol, and Workflow," in IEEE Power and Energy Magazine, vol. 23, no. 5, pp.
93-101, 2025.
[2] Subir Majumder, et al. "Exploring the capabilities and limitations of large language models in
the electric energy sector." Joule 8.6 (2024): 1544-1549.
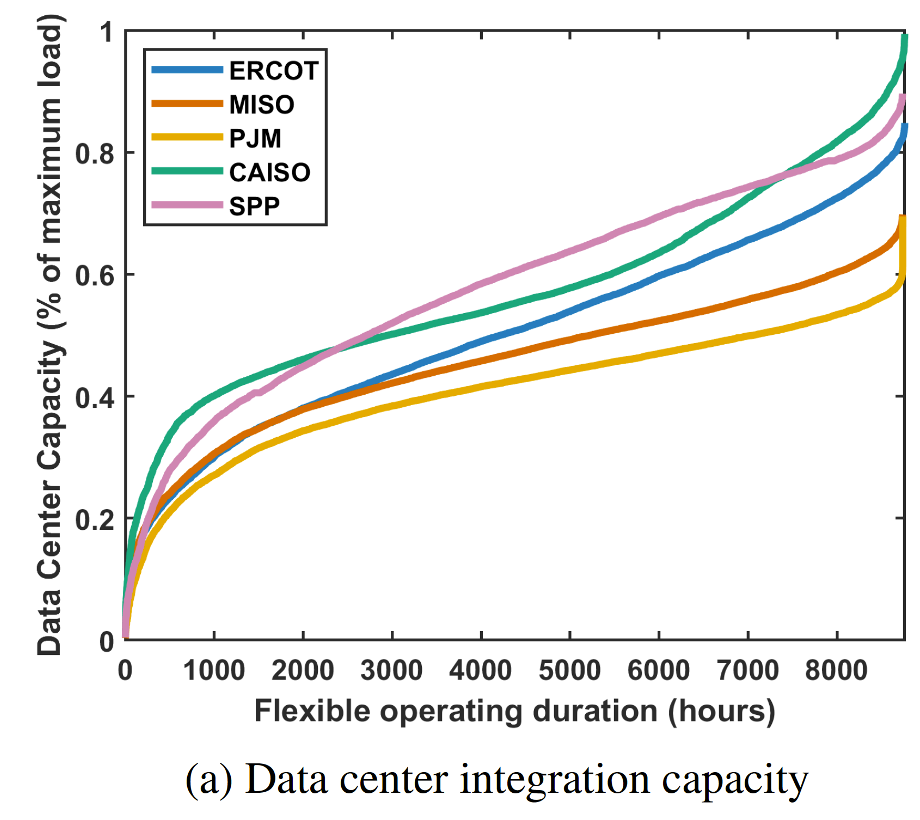
The race
toward artificial general intelligence (AGI) demands unprecedented electricity supply. But how much
can existing electric grids—particularly in the United States—integrate right now? We quantify a
feasibility envelope that yields theoretical upper bounds on the data center capacity that independent
sys-
tem operators and regional transmission organizations (ISOs/RTOs) could integrate without
generation or transmission network upgrades.
[1] Le
Xie, Dongjoo
Kim, Lin Dong. “AI Data Center-Grid Interconnection: Theoretical Limits Now and
Reform Needed Tomorrow”, 2025, Working Paper.
[2] Ali Menati, et al. "High resolution modeling and analysis of cryptocurrency mining’s impact on
power grids: Carbon footprint, reliability, and electricity price." Advances in Applied Energy 10 (2023): 100136.
Advanced AI algorithms for power system operation and control aim to enable adaptive learning of grid dynamics while ensuring safe, explainable operations. They enhance reliability and stability by increasing power throughput, enabling fast fault detection, and improving forecasting accuracy. These advancements optimize energy distribution, support renewable integration, and foster a resilient, data-driven grid.
[1] Amit
Jena, Na Li, and Le Xie. "LILAD: Learning In-context Lyapunov-stable Adaptive Dynamics Models." AAAI
2025, Oral.
[2] Amit Jena, Dileep Kalathil, and Le Xie. "Meta-learning-based adaptive stability certificates
for dynamical systems." AAAI 2024.
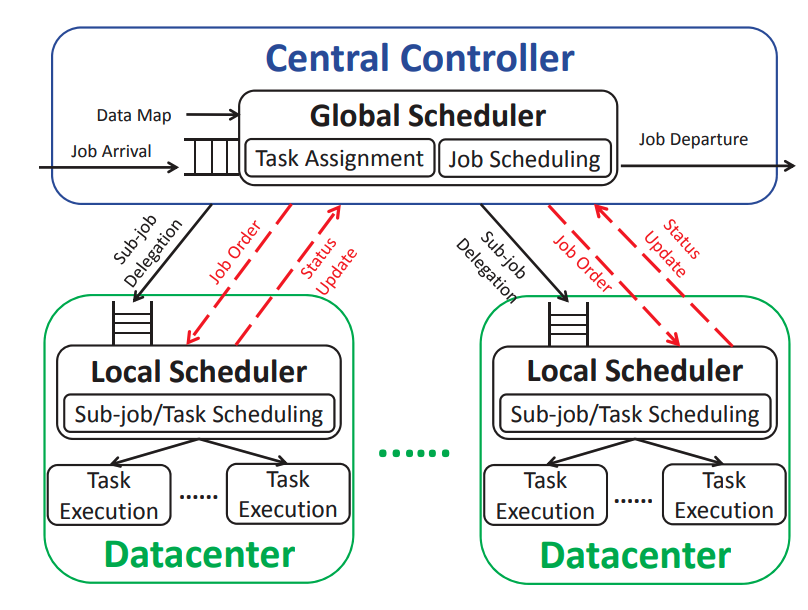
System-level energy-aware computing focuses on optimizing computational tasks to align with electricity demand and pricing fluctuations. Traditional scheduling strategies often rely on immediate demand and price signals without integrating energy forecasts or considering unique source properties. A system-level energy-aware model requires a scheduler responsive to real-time conditions and informed by long-term energy forecasts.
[1]
Chien-Chun Hung, Leana Golubchik, and Minlan Yu. "Scheduling jobs across geo-distributed
datacenters." Proceedings of the Sixth ACM Symposium on Cloud
Computing, 2015.